從網路來源和 API 擷取資料
Kotlin Notebook 提供了一個強大的平台,用於存取和操作來自各種網路來源和 API 的資料。 它通過提供一個可視化的迭代環境來簡化資料提取和分析任務,使每個步驟都清晰明瞭。這使得它在探索不熟悉的 API 時特別有用。
當與 Kotlin DataFrame 函式庫 結合使用時,Kotlin Notebook 不僅使您能夠連接和獲取來自 API 的 JSON 資料,還有助於重塑這些資料,以進行全面的分析和視覺化。
如需 Kotlin Notebook 範例,請參閱 GitHub 上的 DataFrame 範例。
開始之前
-
下載並安裝最新版本的 IntelliJ IDEA Ultimate。
-
在 IntelliJ IDEA 中安裝 Kotlin Notebook 外掛程式。
或者,從 IntelliJ IDEA 中的 Settings(設定) | Plugins(外掛程式) | Marketplace(市集) 存取 Kotlin Notebook 外掛程式。
-
選擇 File(檔案) | New(新增) | Kotlin Notebook 來建立一個新的 Kotlin Notebook。
-
在 Kotlin Notebook 中,執行以下命令來匯入 Kotlin DataFrame 函式庫:
%use dataframe
從 API 獲取資料
使用 Kotlin Notebook 和 Kotlin DataFrame 函式庫從 API 獲取資料,是通過 .read() 函式實現的,該函式與 從檔案中檢索資料(如 CSV 或 JSON)類似。
但是,在處理基於網路的來源時,您可能需要額外的格式化,以將原始 API 資料轉換為結構化的格式。
讓我們看一個從 YouTube Data API 獲取資料的範例:
-
開啟您的 Kotlin Notebook 檔案 (
.ipynb)。 -
匯入 Kotlin DataFrame 函式庫,這對於資料操作任務至關重要。 這可以通過在程式碼儲存格中執行以下命令來完成:
%use dataframe -
在一個新的程式碼儲存格中安全地新增您的 API 金鑰,這對於驗證對 YouTube Data API 的請求是必要的。 您可以從 credentials tab(憑證選項卡) 獲取您的 API 金鑰:
val apiKey = "YOUR-API_KEY" -
建立一個 load 函式,該函式接收一個路徑作為字串,並使用 DataFrame 的
.read()函式從 YouTube Data API 獲取資料:fun load(path: String): AnyRow = DataRow.read("https://www.googleapis.com/youtube/v3/$path&key=$apiKey") -
將獲取的資料組織成行,並通過
nextPageToken處理 YouTube API 的分頁。 這確保您收集跨多個頁面的資料:fun load(path: String, maxPages: Int): AnyFrame {
// Initializes a mutable list to store rows of data.
val rows = mutableListOf<AnyRow>()
// Sets the initial page path for data loading.
var pagePath = path
do {
// Loads data from the current page path.
val row = load(pagePath)
// Adds the loaded data as a row to the list.
rows.add(row)
// Retrieves the token for the next page, if available.
val next = row.getValueOrNull<String>("nextPageToken")
// Updates the page path for the next iteration, including the new token.
pagePath = path + "&pageToken=" + next
// Continues loading pages until there's no next page.
} while (next != null && rows.size < maxPages)
// Concatenates and returns all loaded rows as a DataFrame.
return rows.concat()
} -
使用先前定義的
load()函式來獲取資料,並在一個新的程式碼儲存格中建立一個 DataFrame。 此範例獲取與 Kotlin 相關的資料,或者在本例中是影片,每頁最多 50 個結果,最多 5 頁。 結果儲存在df變數中:val df = load("search?q=kotlin&maxResults=50&part=snippet", 5)
df -
最後,提取並串聯 DataFrame 中的項目:
val items = df.items.concat()
items
清理和完善資料
清理和完善資料是準備用於分析的資料集的關鍵步驟。Kotlin DataFrame 函式庫
為這些任務提供了強大的功能。諸如 move、
concat、select、
parse 和 join
之類的方法有助於組織和轉換您的資料。
讓我們來看一個範例,其中資料已經 使用 YouTube 的資料 API 獲取。 目標是清理和重組資料集,為深入分析做準備:
-
您可以首先重新組織和清理您的資料。這包括將某些列移動到新的標題下,並刪除不必要的列以使其更清晰:
val videos = items.dropNulls { id.videoId }
.select { id.videoId named "id" and snippet }
.distinct()
videos -
從清理後的資料中分塊 IDs,並載入相應的影片統計資訊。這包括將資料分成更小的批次,並獲取其他詳細資訊:
val statPages = clean.id.chunked(50).map {
val ids = it.joinToString("%2C")
load("videos?part=statistics&id=$ids")
}
statPages -
串聯獲取的統計資訊並選擇相關的列:
val stats = statPages.items.concat().select { id and statistics.all() }.parse()
stats -
將現有的清理後的資料與新獲取的統計資訊連接起來。這將兩個資料集合併到一個全面的 DataFrame 中:
val joined = clean.join(stats)
joined
此範例示範如何使用 Kotlin DataFrame 的各種函式來清理、重新組織和增強您的資料集。 每個步驟都旨在完善資料,使其更適合於 深入分析。
在 Kotlin Notebook 中分析資料
在您成功 獲取 並 清理和完善資料 使用來自 Kotlin DataFrame 函式庫 的函式後,下一步 是分析這個準備好的資料集,以提取有意義的見解。
諸如 groupBy 用於分類資料、
sum 和 maxBy 用於
summary statistics(摘要統計) 以及 sortBy 用於
排序資料之類的方法特別有用。
這些工具使您可以有效地執行複雜的資料分析任務。
讓我們來看一個範例,使用 groupBy 按頻道對影片進行分類,使用 sum 計算每個類別的總觀看次數,
並使用 maxBy 找到每個群組中最新或觀看次數最多的影片:
-
通過設定引用來簡化對特定列的訪問:
val view by column<Int>() -
使用
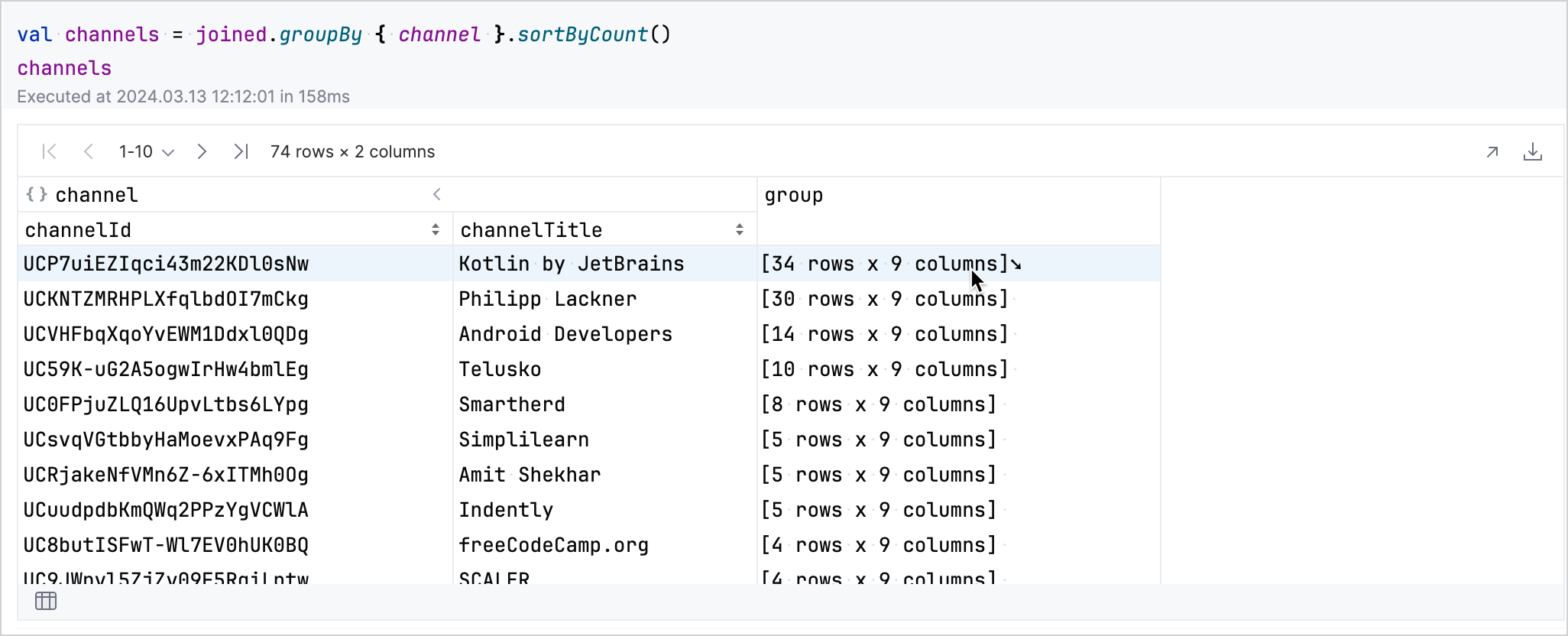
groupBy方法按channel列對資料進行分組並對其進行排序。val channels = joined.groupBy { channel }.sortByCount()
在結果表格中,您可以交互式地瀏覽資料。單擊與頻道對應的行的 group 欄位
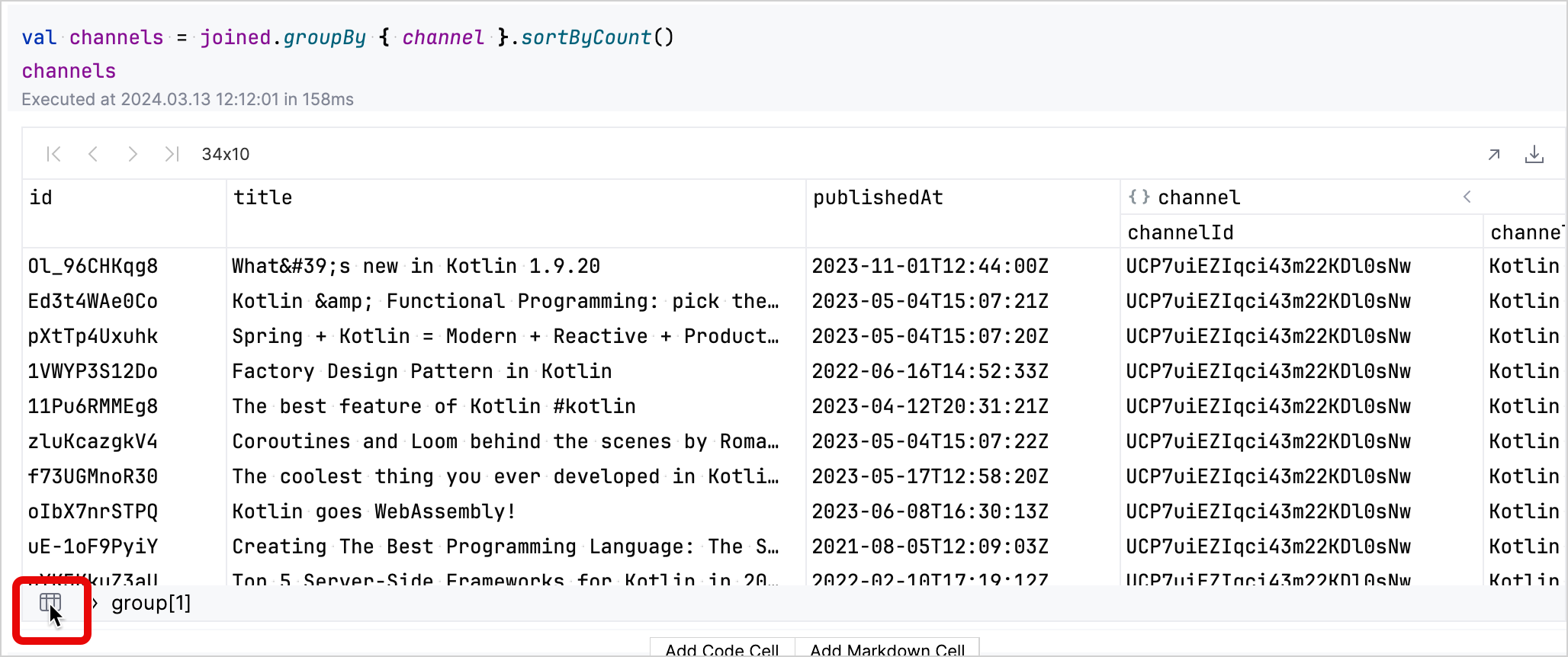
展開該行以顯示有關該頻道影片的更多詳細資訊。
您可以單擊左下角的表格圖示返回到分組的資料集。
-
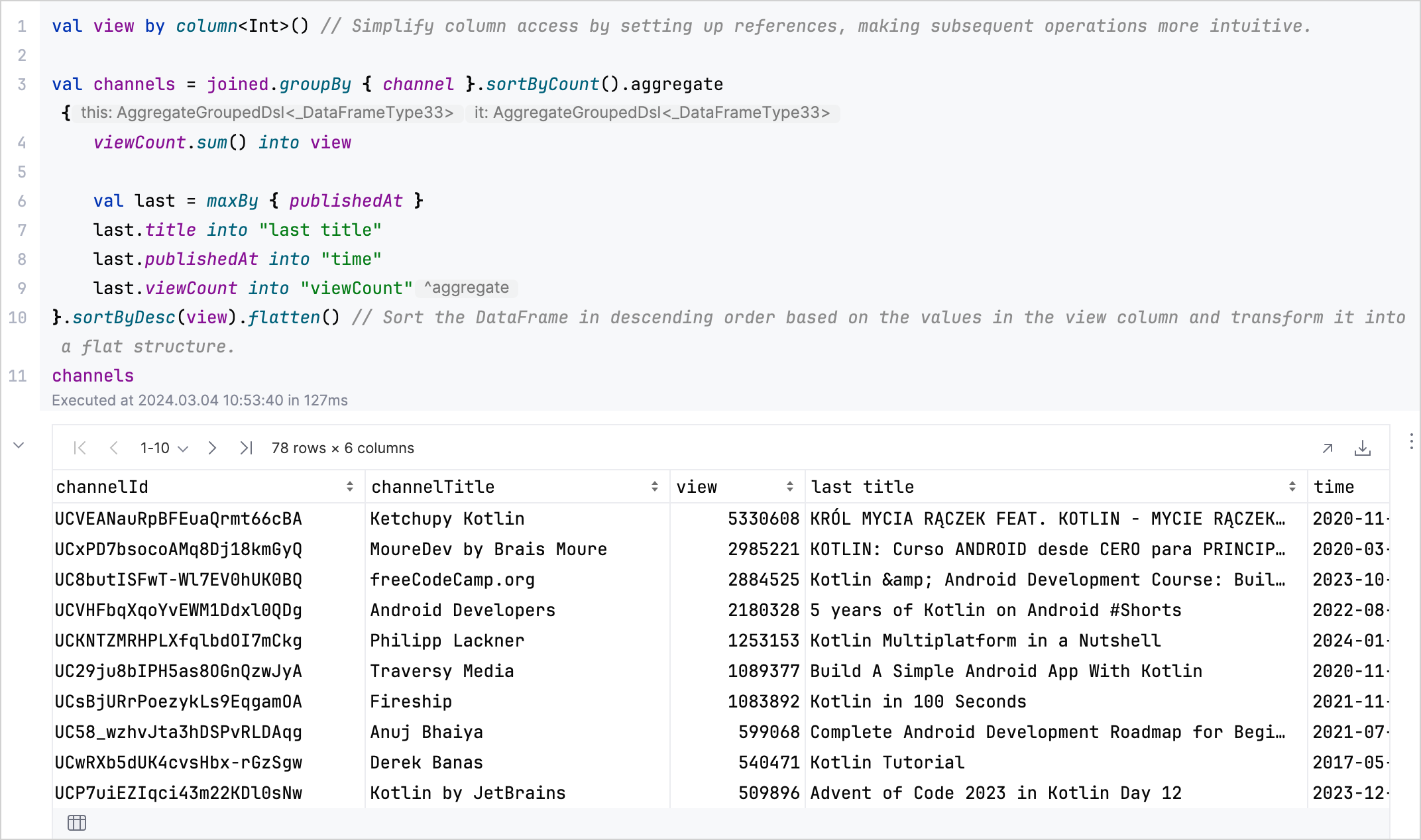
使用
aggregate、sum、maxBy和flatten建立一個 DataFrame,總結每個 頻道的總觀看次數及其最新或觀看次數最多的影片的詳細資訊:val aggregated = channels.aggregate {
viewCount.sum() into view
val last = maxBy { publishedAt }
last.title into "last title"
last.publishedAt into "time"
last.viewCount into "viewCount"
// Sorts the DataFrame in descending order by view count and transform it into a flat structure.
}.sortByDesc(view).flatten()
aggregated
分析結果:
如需更高級的技術,請參閱 Kotlin DataFrame 文件。
接下來
- 使用 Kandy 函式庫 探索資料視覺化
- 在 Data visualization in Kotlin Notebook with Kandy(使用 Kandy 在 Kotlin Notebook 中進行資料視覺化) 中尋找有關資料視覺化的其他資訊
- 如需 Kotlin 中用於資料科學和分析的工具和資源的廣泛概述,請參閱 Kotlin and Java libraries for data analysis(用於資料分析的 Kotlin 和 Java 函式庫)