在 Kotlin Notebook 中使用 Kandy 進行資料視覺化
Kotlin 提供了一種全方位的解決方案,用於強大且靈活的數據視覺化,提供了一種直觀的方式來呈現和探索數據,然後再深入研究複雜的模型。
本教學示範了如何使用 Kotlin Notebook 在 IntelliJ IDEA 中建立不同的圖表類型,搭配 Kandy 和 Kotlin DataFrame 函式庫。
開始之前
-
下載並安裝最新版本的 IntelliJ IDEA Ultimate。
-
在 IntelliJ IDEA 中安裝 Kotlin Notebook plugin。
或者,從 IntelliJ IDEA 內的 Settings | Plugins | Marketplace 存取 Kotlin Notebook 插件 (plugin)。
-
選擇 File | New | Kotlin Notebook 來建立一個新的 Notebook。
-
在您的 Notebook 中,執行以下命令來匯入 Kandy 和 Kotlin DataFrame 函式庫:
%use kandy
%use dataframe
建立 DataFrame (數據幀)
首先,建立包含要視覺化的記錄的 DataFrame (數據幀)。此 DataFrame (數據幀) 儲存了三個城市:柏林、馬德里和卡拉卡斯,每月平均溫度的模擬數字。
使用 Kotlin DataFrame 函式庫中的 dataFrameOf() 函式來生成 DataFrame (數據幀)。在 Kotlin Notebook 中執行以下程式碼片段:
// months 變數儲存了一年 12 個月的列表
val months = listOf(
"January", "February",
"March", "April", "May",
"June", "July", "August",
"September", "October", "November",
"December"
)
// tempBerlin、tempMadrid 和 tempCaracas 變數儲存了每個月的溫度值列表
val tempBerlin =
listOf(-0.5, 0.0, 4.8, 9.0, 14.3, 17.5, 19.2, 18.9, 14.5, 9.7, 4.7, 1.0)
val tempMadrid =
listOf(6.3, 7.9, 11.2, 12.9, 16.7, 21.1, 24.7, 24.2, 20.3, 15.4, 9.9, 6.6)
val tempCaracas =
listOf(27.5, 28.9, 29.6, 30.9, 31.7, 35.1, 33.8, 32.2, 31.3, 29.4, 28.9, 27.6)
// df 變數儲存了一個包含三列的 DataFrame (數據幀),包括月份、溫度和城市的記錄
val df = dataFrameOf(
"Month" to months + months + months,
"Temperature" to tempBerlin + tempMadrid + tempCaracas,
"City" to List(12) { "Berlin" } + List(12) { "Madrid" } + List(12) { "Caracas" }
)
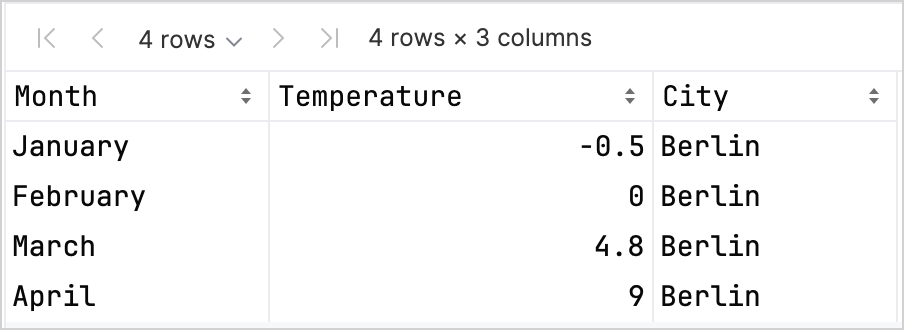
查看前四行,探索新 DataFrame (數據幀) 的結構:
df.head(4)
您可以看到 DataFrame (數據幀) 有三列:Month (月份)、Temperature (溫度) 和 City (城市)。 DataFrame (數據幀) 的前四行包含從一月到四月在柏林的溫度記錄:
有多種選項可以存取欄位的記錄,這有助於您在使用 Kandy 和 Kotlin DataFrame 函式庫時提高類型安全性。 有關更多資訊,請參閱 Access APIs。
建立折線圖
讓我們使用上一節中的 df DataFrame (數據幀) 在 Kotlin Notebook 中建立一個折線圖。
使用 Kandy 函式庫中的 plot() 函式。在 plot() 函式中,指定圖表的類型(在本例中為 line),以及 X 軸和 Y 軸的值。您可以自訂顏色和尺寸:
df.plot {
line {
// 存取用於 X 軸和 Y 軸的 DataFrame (數據幀) 的欄位
x(Month)
y(Temperature)
// 存取用於類別的 DataFrame (數據幀) 的欄位,並為這些類別設定顏色
color(City) {
scale = categorical("Berlin" to Color.PURPLE, "Madrid" to Color.ORANGE, "Caracas" to Color.GREEN)
}
// 自訂線的尺寸
width = 1.5
}
// 自訂圖表的版面配置尺寸
layout.size = 1000 to 450
}
這是結果:

建立散佈圖
現在,讓我們在散佈(散點)圖中視覺化 df DataFrame (數據幀)。
在 plot() 函式中,指定 points 圖表類型。新增 X 軸和 Y 軸的值以及 df 欄位中的類別值。
您還可以為圖表新增標題:
df.plot {
points {
// 存取用於 X 軸和 Y 軸的 DataFrame (數據幀) 的欄位
x(Month) { axis.name = "Month" }
y(Temperature) { axis.name = "Temperature" }
// 自訂點的尺寸
size = 5.5
// 存取用於類別的 DataFrame (數據幀) 的欄位,並為這些類別設定顏色
color(City) {
scale = categorical("Berlin" to Color.LIGHT_GREEN, "Madrid" to Color.BLACK, "Caracas" to Color.YELLOW)
}
}
// 新增圖表標題
layout.title = "Temperature per month"
}
這是結果:

建立長條圖
最後,讓我們使用與先前圖表相同的數據,建立一個按城市分組的長條圖。 對於顏色,您也可以使用十六進位程式碼:
// 按城市分組
df.groupBy { City }.plot {
// 新增圖表標題
layout.title = "Temperature per month"
bars {
// 存取用於 X 軸和 Y 軸的 DataFrame (數據幀) 的欄位
x(Month)
y(Temperature)
// 存取用於類別的 DataFrame (數據幀) 的欄位,並為這些類別設定顏色
fillColor(City) {
scale = categorical(
"Berlin" to Color.hex("#6F4E37"),
"Madrid" to Color.hex("#C2D4AB"),
"Caracas" to Color.hex("#B5651D")
)
}
}
}
這是結果:

接下來做什麼
- 在 Kandy 函式庫文件 中探索更多圖表示例
- 在 Lets-Plot 函式庫文件 中探索更進階的繪圖選項
- 在 Kotlin DataFrame 函式庫文件 中尋找有關建立、探索和管理數據幀的其他資訊
- 在此 YouTube 影片 中瞭解有關 Kotlin Notebook 中數據視覺化的更多資訊